Carbon Dioxide (CO2) vs Carbon Monoxide (CO), what you need to know!
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) are both chemical compounds containing carbon and oxygen atoms. Despite their similar names and some shared characteristics, these two substances have distinct properties, sources, and effects on living organisms and the environment. This document will explore the key differences between carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
PDF DOWNLOAD

CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
- Chemical Formula:
- Carbon dioxide: CO2
- Carbon monoxide: CO
- Composition:
- Carbon dioxide consists of one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom bonded to one oxygen atom.
SOURCES AND PRODUCTION
- Sources:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Produced during respiration in animals and combustion processes.
- Released by natural sources like volcanic eruptions and cellular respiration in plants.
- A key greenhouse gas produced by human activities such as burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) and deforestation.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Primarily produced through incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels, like gasoline, wood, and natural gas.
- Commonly found in vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and incomplete home heating combustion.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- State at Room Temperature:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Gaseous at room temperature.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Gaseous at room temperature.
- Colour and Odour:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Colourless, odourless gas.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Colourless, odourless gas, making it particularly dangerous as it cannot be detected by smell.
TOXICITY AND HEALTH EFFECTS
- Toxicity:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Generally not toxic in normal concentrations, but high levels can lead to asphyxiation by displacing oxygen in the air.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Highly toxic, even at low concentrations. It binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells, reducing the blood’s ability to carry oxygen, leading to carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Symptoms of Exposure:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Typically causes shortness of breath, dizziness, and can be life-threatening at high concentrations.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Symptoms include headache, nausea, confusion, and can lead to unconsciousness or death in severe cases.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
- Greenhouse Gas Effect:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Considered a major greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming and climate change due to its ability to trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Has a limited role as a greenhouse gas and is less significant in terms of its contribution to global warming.
DETECTION AND MONITORING
- Detection:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Detectable using infrared gas analysers and chemical test kits.
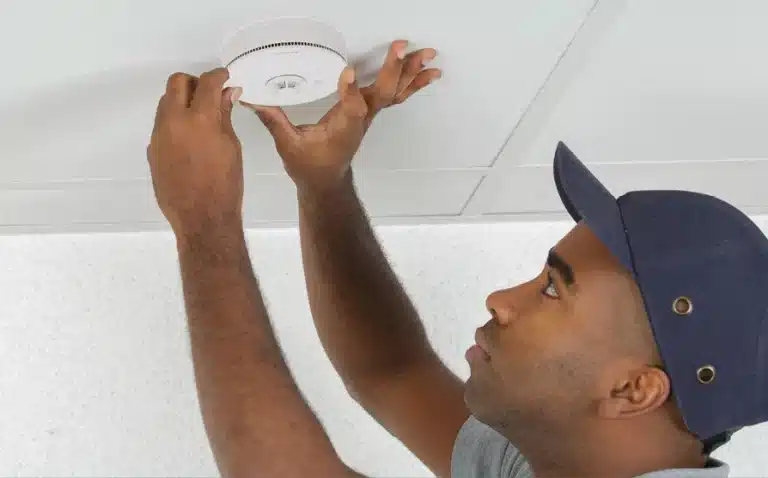
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Detectable using carbon monoxide detectors, which are essential for safety in homes and workplaces.
In summary, while both carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) contain carbon and oxygen atoms, they have distinct chemical compositions, sources, physical properties, health effects, and environmental impacts. Carbon dioxide is primarily known as a greenhouse gas, while carbon monoxide is a toxic gas produced by incomplete combustion processes. Understanding the differences between these two compounds is crucial for both safety and environmental awareness.